Why You Should Keep Good Records
1 min read
Table of Contents
Recordkeeping is the orderly and disciplined practice of storing business-related documents
- A system that allows you to collect information about your business activities, access it when needed, summarize it for reporting, and analyze it for business decision making
- One of the most important responsibilities as a small business owner
- A business’s success depends on creating and maintaining an effective record system
- The importance of measurement: To manage a business you must be able to measure activity
- Helps with detailed tracking of revenues and expenses, planning, legal compliance, and tax return preparation (federal, state, and local)
Audience for Your Records & Reports: #
- You, so that you can carry out operations, prepare periodic reports, and file income tax returns
- Partners or investors so that financial statements can be prepared and financial positions and results of operations can be monitored
- Bankers so that loan applications can be reviewed and loan servicing can be monitored
- IRS and state authorities so that tax returns and other tax-related documents can be prepared and issued
Accounting Software: #
- Complete financial recordkeeping system
- Allows for recording and posting all the transactions of your business, with a preset or easily adapted chart of accounts
- Automatically generate reports and graphs, such as balance sheets, profit and loss statements, and cash flow statements
- QuickBooks is most popular for small businesses
- Desktop system with files residing on the computer’s hard drive
- User must back up and protect data
- Subscription solutions (e.g., QuickBooks Online)
- Accounting software that is hosted on remote servers
- Data is processed and stored in the cloud
- Password protected with automatic backup of data
- Access real-time data from anywhere with an Internet connection––Access from any device, including laptops, smart phones and tablets
- Routine maintenance and updates to the software are managed by the SaaS (Software as a Service) provider
Accounting Records: #
Accounting records take many forms: source documents, journals, ledgers, trial balances, and financial statements
- Evidence of a business transaction
- Important starting point of the audit trail
- An audit trail can be either a paper- or digital-based trail showing a documented history of a transaction
- An audit trail allows an auditor to follow the financial data from its original creation or source document (invoice, receipt, voucher, etc.) to the general ledger
- Examples of source documents:
- Invoices
- Other evidence of income, such as copies of checks, receipts, and bank statements
- Expense documentation
- Canceled checks that identify the payee, amount, and proof of payment/electronic funds transferred
- Cash register tapes
- Account statements
- Credit card receipts and statements
- Invoices
- Petty cash slips for small cash payments
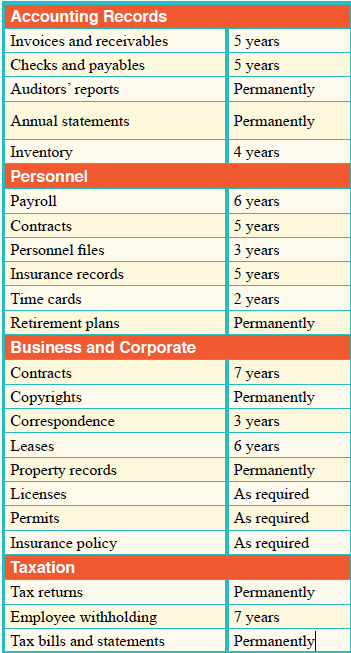
Record Retention Schedule: #
Record retention guidelines recommended by the US Small Business Administration
Powered by BetterDocs



